Do I have a tooth infection? Symptoms and treatment options
A tooth infection, also known as a tooth abscess, can be a painful and potentially serious dental problem that requires immediate attention. But how do you know if you have a tooth infection? This blog post will explore the common symptoms of dental infection and the various treatment options available to alleviate this dental concern.
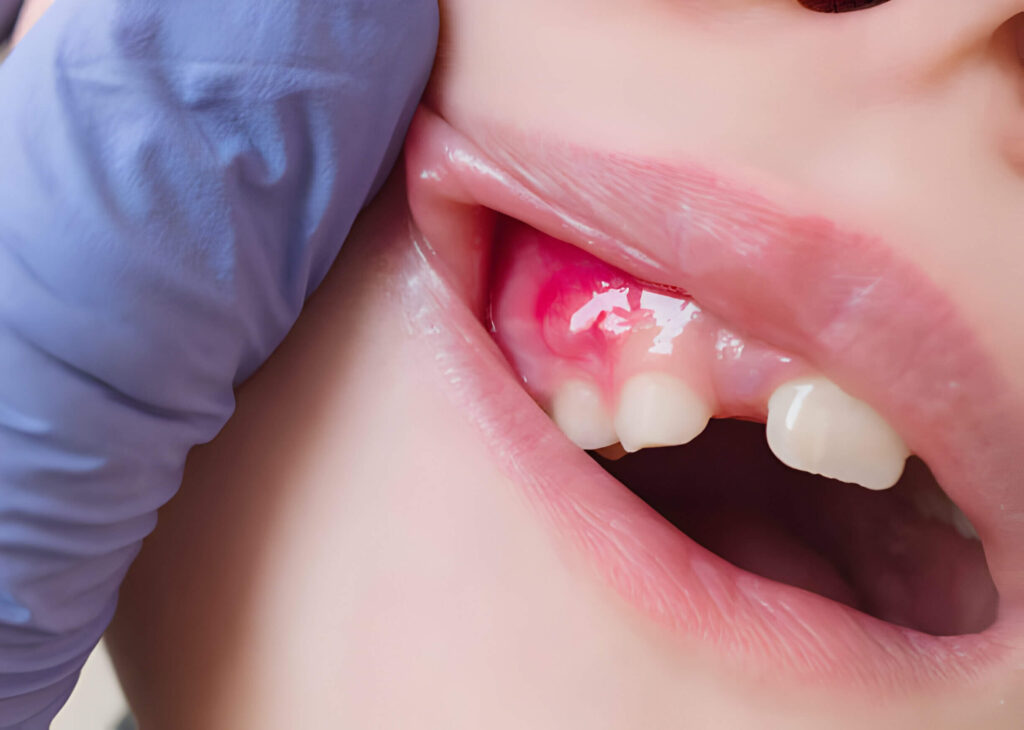
Symptoms of a tooth infection:
- Severe toothache: One of the most common and noticeable symptoms of a tooth infection is a painful, throbbing toothache. The pain can be constant or intermittent and can be especially severe when you bite down on the affected tooth.
- Swelling and redness: A tooth infection can cause localized swelling in the affected area of your mouth. You may also notice redness and tenderness in your gums around the infected tooth.
- Pus Formation: The presence of pus near the affected tooth is a clear sign of infection. Pus can have an unpleasant taste and smell and can drain from a small bump on your gums, known as a dental abscess.
- Fever and general malaise: Dental infections can sometimes cause fever, general malaise and malaise. This happens when the infection spreads outside the tooth.
- Bad breath or bad taste: An unpleasant taste or persistent bad breath in your mouth can also indicate a tooth infection. Bad breath is usually the result of the condition.
Difference between tooth infection and cavity:
Tooth infection and cavities are both dental problems, but they differ in severity and amount of damage. Cavities, also known as tooth decay, occur when enamel—the outer layer of a tooth—is eroded by bacteria and acid, resulting in a small hole. It is a localized problem that can often be solved with a dental filling, preventing further decay.
Dental infections, on the other hand, occur when bacteria penetrate deep into the tooth, reaching the pulp, which contains nerves and blood vessels. This can lead to inflammation, pain, and possible complications. While a cavity is a mild form of tooth decay, a tooth infection is a more serious condition that may require a root canal or, in severe cases, an extraction.
Treatment options for tooth infection:
- Antibiotics: In mild cases of tooth infection, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to clear up the infection. However, antibiotics alone will not completely solve the problem; Further dental treatment is usually required.
- Root Canal Therapy: A root canal procedure may be necessary if the infection has reached the tooth’s pulp. During a root canal, the infected pulp is removed, and the tooth is cleaned, disinfected, and sealed to prevent further infection.
- Drainage of Abscess: If a dental abscess has developed, your dentist may need to drain it to relieve pain and eliminate the infection. This is usually a quick and straightforward process.
- Tooth Extraction: In severe cases where the tooth is severely damaged and cannot be saved, your dentist may recommend extraction of the infected tooth. After the extraction, you can discuss tooth replacement options, such as dental implants or bridges.
- Pain management: During treatment, your dentist may recommend over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribe stronger medications to control pain and discomfort.
Avoiding dental infections:
Prevention is always better than cure. To reduce your risk of dental infection, maintain good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups. Avoid sugary foods and drinks and consider dental sealants and fluoride treatments to strengthen your teeth.
It is important to recognize the symptoms of dental infection early for timely treatment and prevention of complications. If you suspect a tooth infection based on the above symptoms, do not hesitate to contact your dentist for a proper evaluation and treatment plan. Remember that dental infections should not be ignored, as they can lead to more serious health problems if left untreated.
Contact Aurora Smiles, For your dental Care!
